From the operation principle of heat pump, can be divided into vapor compression heat pump, absorption heat pump, semiconductor heat pump and chemical heat pump;
From the hot water heating method and characteristics, can be divided into split static heating type, circulation heating type and direct heating type;
From the source of heat source, can be divided into water-source heat pumps, soil-source heat pumps, wastewater-source heat pumps, air-source heat pumps, solar heat pumps;
From the heat pump drive energy, can be divided into electric heat pumps, fuel or gas heat pumps, steam (absorption) heat pumps and so on;
From the use of points up, can be divided into open that is hot and heat storage type.
Different types of heat pumps:
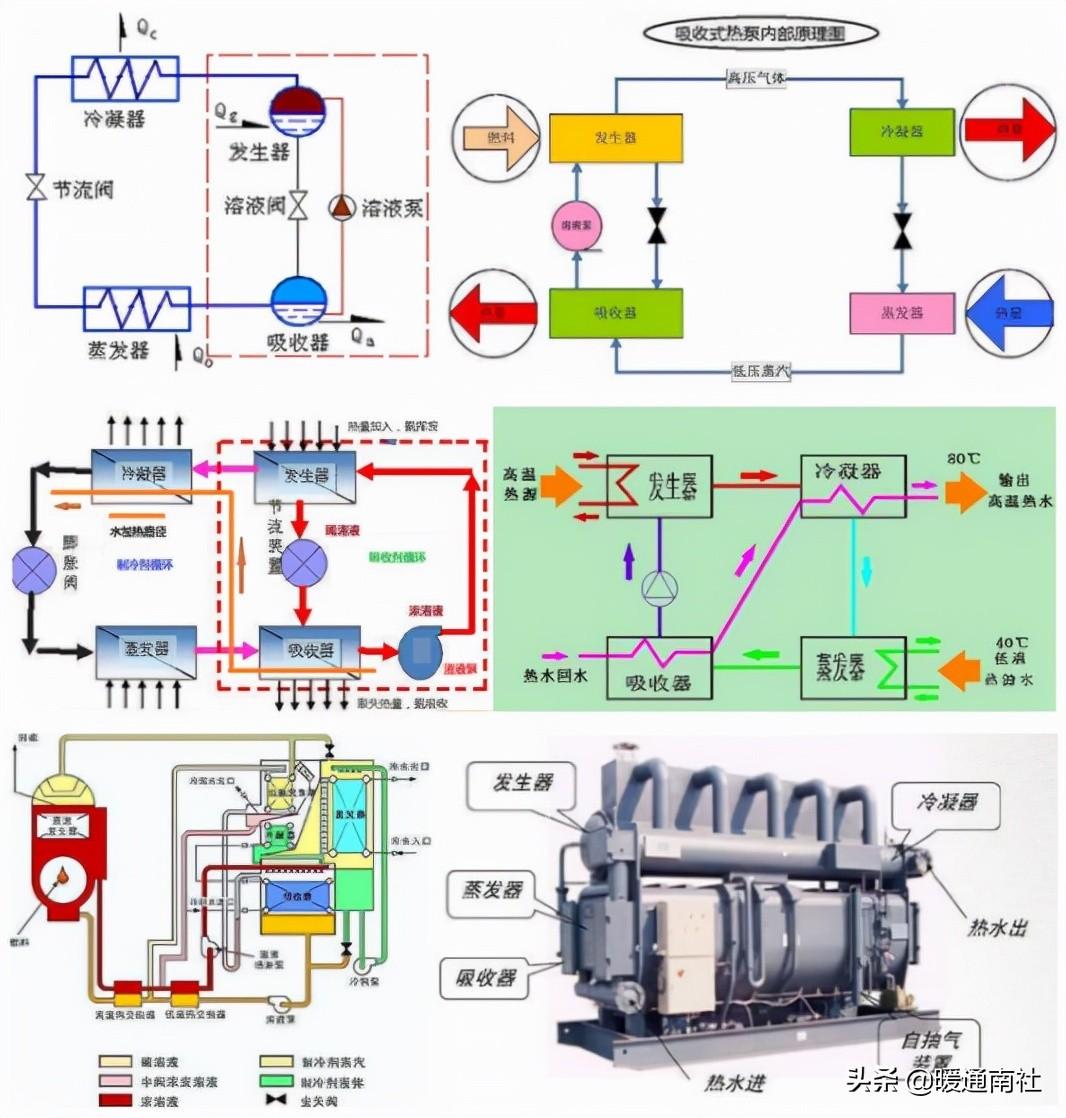
Absorption heat pumps:
Absorption heat pump does not have a compressor, it is powered by heat energy, using some some kind of solution to another solution of the strong absorbency, to achieve the transfer of heat from the evaporator to the condenser.
Since absorption refrigeration (heat pump) can operate with heat of lower temperature, it is an effective means of utilizing low-grade heat energy such as industrial waste heat.
Absorption heat pump consists of generator, absorber, throttle valve, condenser, evaporator, liquid valve and solution pump, etc. The principle is shown below:
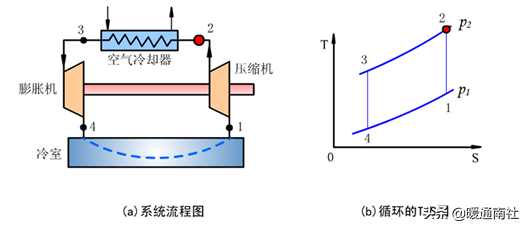
Gas adiabatic expansion refrigeration:
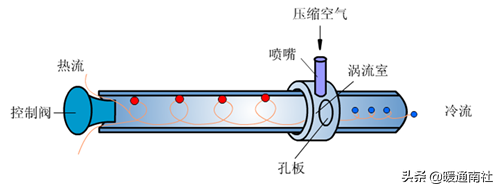
Vortex cooling:
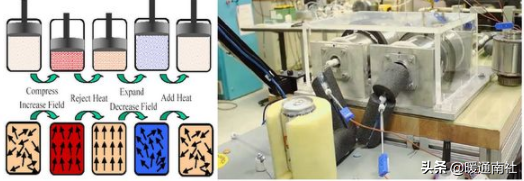
Magnetic refrigeration:
Is the use of magnetic heat effect, also known as magnetic card effect refrigeration.
Magnetothermal effect refers to the fusion refrigeration work material in the isothermal magnetization to the outside world to release heat, and adiabatic demagnetization when the temperature decreases, from the outside world to absorb heat phenomenon. The refrigerant in magnetic refrigeration technology is a solid magnetic material.
If such two adiabatic demagnetization caused by the heat absorption process and adiabatic magnetization caused by the exothermic process with a cycle connected by an external magnetic field, conscious control of the magnetic inertia, you can make the magnetic material constantly from one end of the heat absorption and at the other end of the exothermic, so as to achieve the purpose of refrigeration.
Magnetothermal effect:
Using the magneto-thermal effect of magnetically cooled materials (the basic principle is the magnetization of magnetic materials exothermic and demagnetization heat absorption).
Based on the magneto-thermal effect of materials and certain thermal processes can constitute a magnetic refrigeration cycle.
Semiconductor refrigeration (heat pump):
Semiconductor refrigeration (heat pump), also known as thermoelectric refrigeration (heating), different semiconductors linked into the circuit, when a voltage is applied to its terminals, the different semiconductors will be current between the different semiconductors and accompanied by the phenomenon of thermal movement, the use of this phenomenon and made of the device is called semiconductor refrigeration (heat pump) device;
P, N-type semiconductors used for refrigeration structural principles:
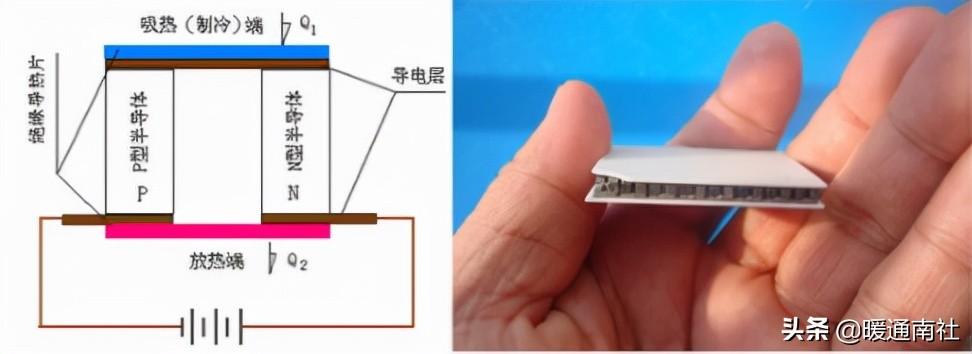
The efficiency of semiconductor refrigeration (heat pump) depends to a large extent on the temperature difference between the hot and cold ends of the thermopile, in the case of a small temperature difference between the hot and cold ends, the efficiency of the semiconductor heat pump is still quite high.
Vapor compression refrigeration principle:
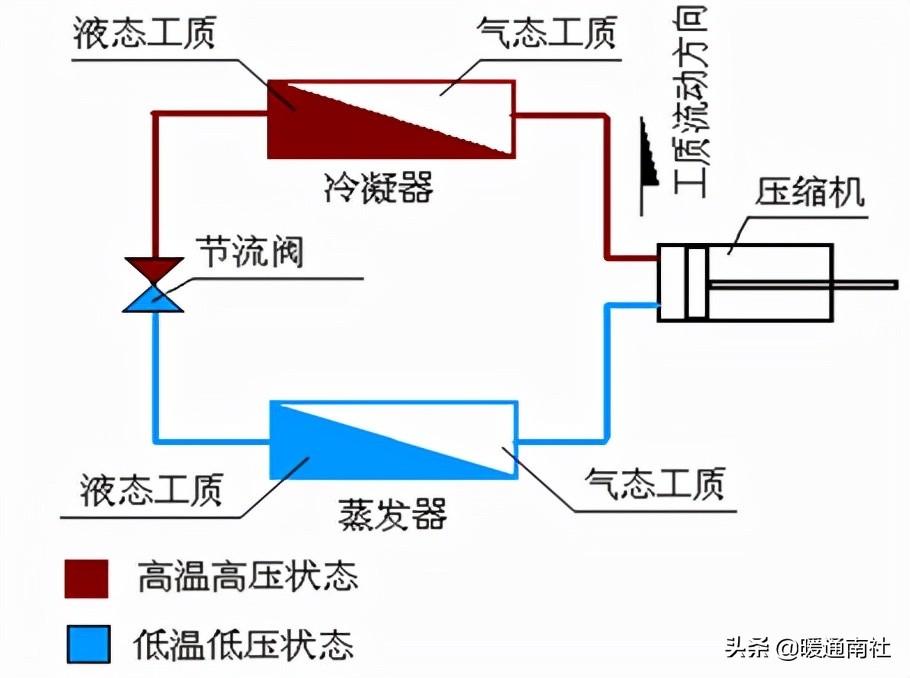
Vapor compression heat pump water heater, no matter which type, its host is composed of four major components: compressor, condenser, throttle and evaporator;
In order to better ensure the normal operation of the heat pump system, the heat pump system must also be set up gas-liquid separator, high and low pressure protectors, over-temperature protectors, automatic controllers, mechanical pressure relief valves, four-way valves, solenoid valves, one-way valves, crankcase plus heat tape, reservoirs, and a large number of other parts.
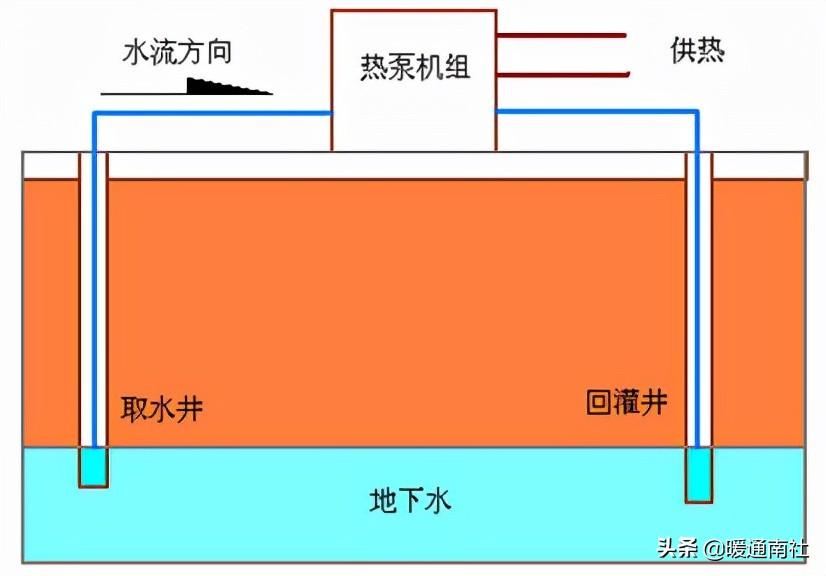
Schematic diagram of water source heat pump using groundwater:
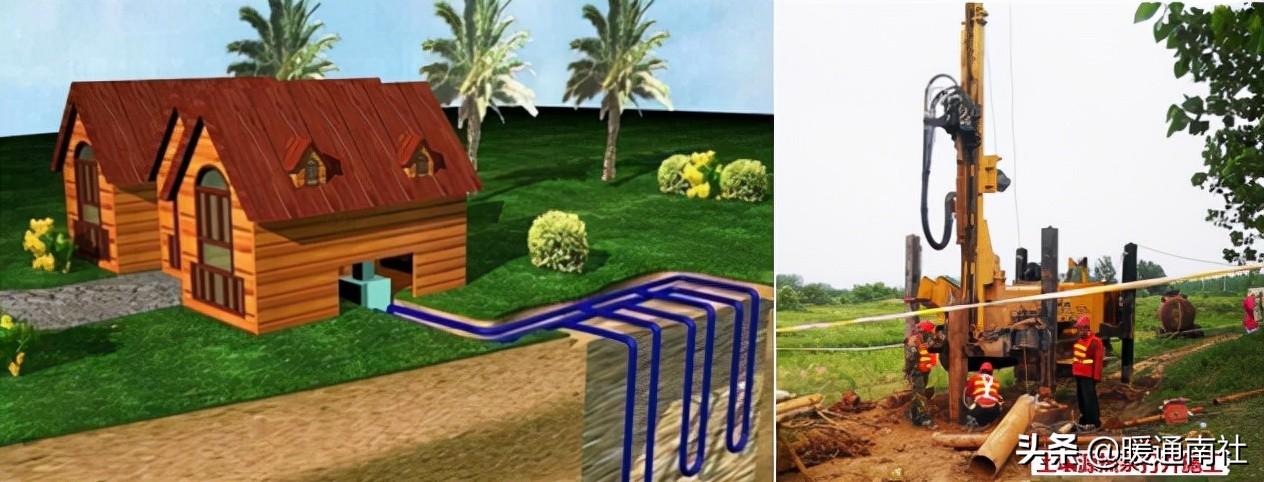
Principle of soil source heat pump system:
It is a heat pump device with soil as the heat source, which buries the soil heat exchanger into the ground, brings out the heat deep in the earth through the heat-carrying agent, and raises the temperature through the heat pump for heating and domestic hot water, the soil-source heat pump avoids the problem of recharging of the groundwater-source heat pump, and at the same time, avoids a series of troubles such as corrosion, scaling and so on of the groundwater, no pollution, and the system is clean, which is the biggest advantage of the soil-source heat pump.
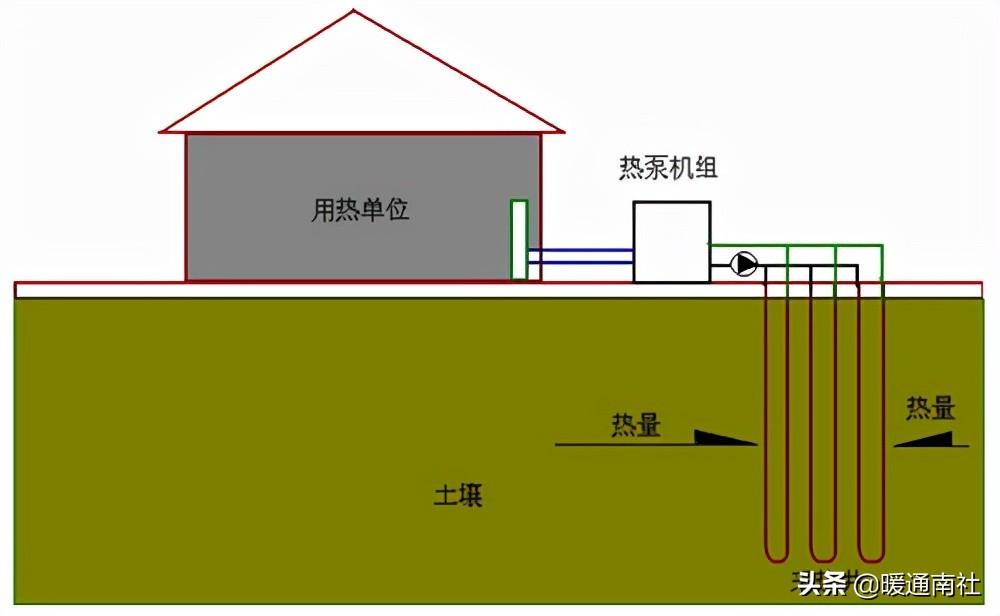
But its application also has the following problems: due to the soil's very poor thermal conductivity, so that the cold end of the soil source heat pump to the soil heat extraction is very difficult.
However, its application also has the following problems: due to the extremely poor thermal conductivity of the soil, making it very difficult to extract heat from the soil at the cold end of the soil source heat pump.

Solar heat pump:
Solar heat pump water heater, is through the direct use of solar radiation and ambient air as the heat source of the heat pump unit, which has two types: that is, the collector plate directly as the evaporator of the "direct expansion", and the solar collector plate absorbed heat through a heat exchanger for evaporation of the "indirect expansion type ". Solar collectors for heat pumps can also be divided into ordinary flat-plate collectors with light-transmitting panels and thermal insulation measures, and collectors with metal plate cores only, which are in direct contact with the air and have the ability to work in cloudy and rainy days, even though they increase heat dissipation losses when there is sunlight.

Air source heat pump water heating unit and main components:
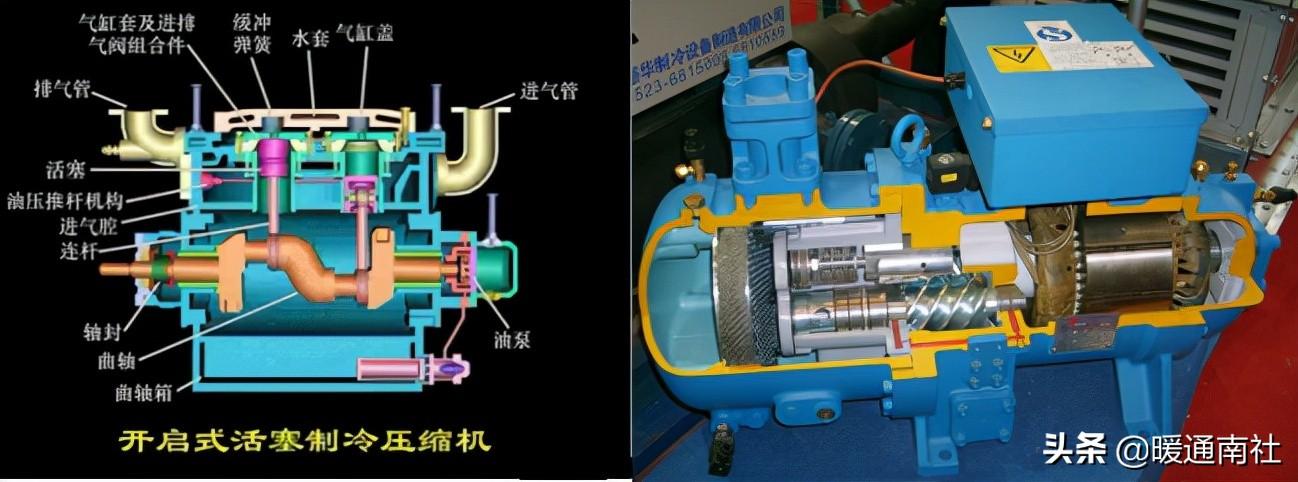
According to the principle of compression, the compressor is roughly divided into two categories: volumetric compressor and velocity compressor;
According to the sealing structure of the compressor classification: the compressor can be divided into three categories: open compressor, semi-closed compressor and fully closed compressor;
Double and single rolling rotor type compressor:
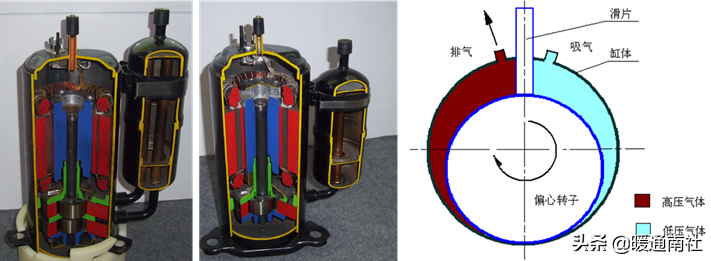
In the current small domestic heat pump water heater series products, occupies the most important position, the vast majority of domestic heat pump water heater are used in this type of compressor.
Rolling rotor compressor running smoothly, large output, low price, in dynamic balance, better than piston performance; double rotor running better;
Unfavorable is that the compressor shell is a high-pressure chamber, the motor winding operation is unfavorable, but also unfavorable to the lubrication .
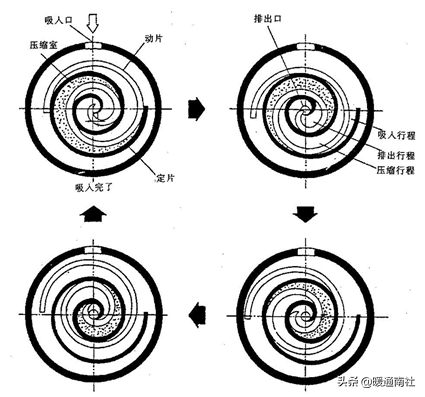
Scroll compressor:
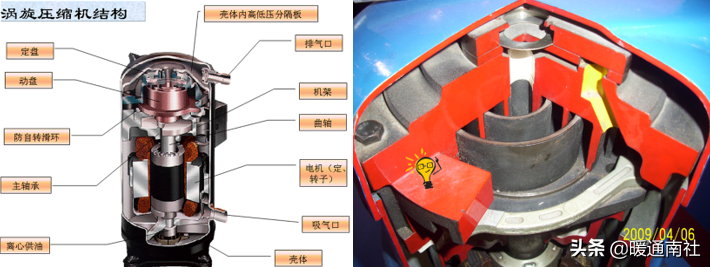
The fixed and moving disks of a scroll compressor:
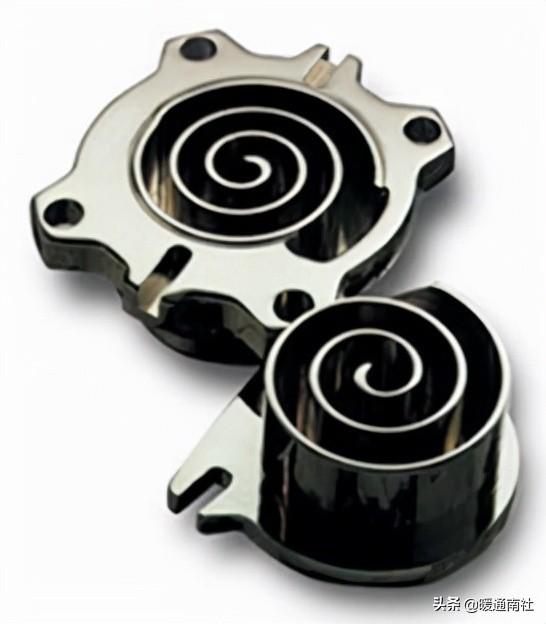

Because of the scroll compressor, its scroll has a number of layers (for example, three layers), therefore, in its rotation process, suction, compression and exhaust processes are carried out simultaneously in different layers of the compression chamber, the formation of a compression chamber to the completion of the exhaust, it is necessary to go through a number of weeks to be able to complete the compression chamber in the outside, the crankshaft rotates every week to complete a suction process, and close to the center part of the compression chamber is constantly carrying out the Exhaust process, compression chamber and adjacent compression chamber pressure difference is smaller, so the torque is balanced, smooth operation, internal leakage is small, high volumetric efficiency. Work is also more reliable.
Scroll compressor shell for the low-pressure chamber.
The function of the main components of the motor: iron core, including stator core and rotor core, used to form the magnetic circuit of the motor;
Stator winding is divided into working winding and starting winding, in order to prevent short-circuiting between each circle (turn), the use of high-strength polyester enameled wire winding, respectively, for the motor to provide working torque and starting torque;
The starting capacitor is used to shift the AC phase for motor starting, and together with the starting winding, it provides the starting torque for the motor rotor;
Motor end caps and bearings play a role in supporting the normal operation of the rotor;
The rotor receives the force of the rotating magnetic field and outputs work;
The chassis locates, encloses, and dissipates heat from the entire motor.
Evaporator and condenser:
Air source heat pump water heater, is to use the air as a heat source to achieve the purpose of "heating" water, directly completed from the air to absorb heat from the device, is the evaporator;
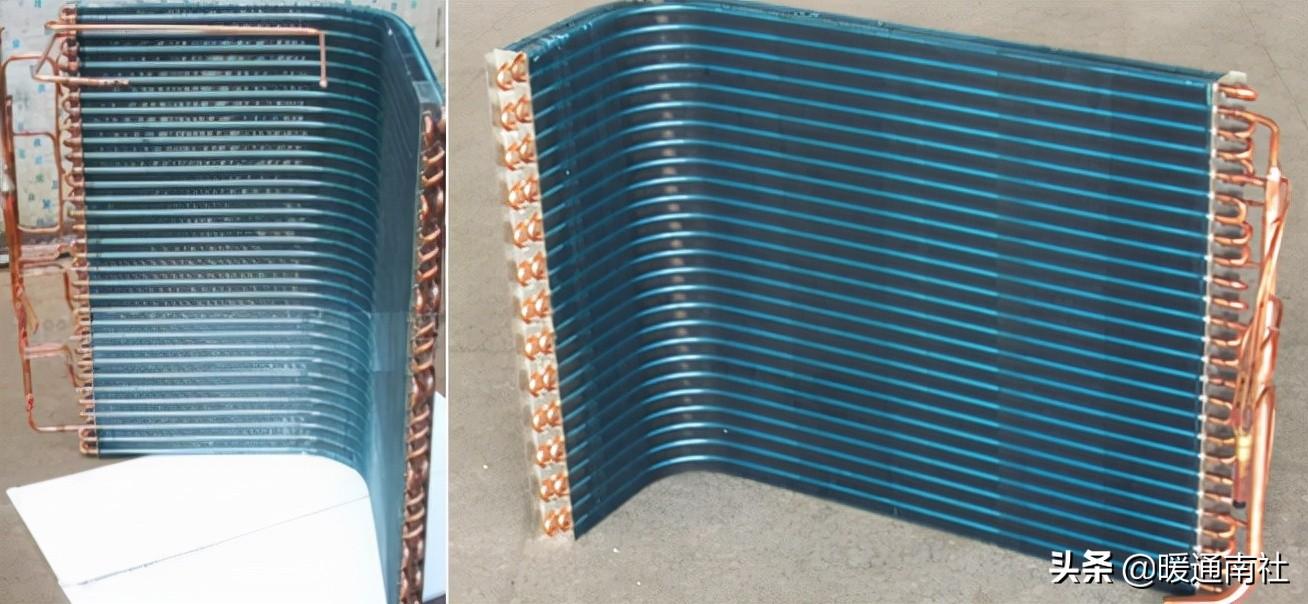
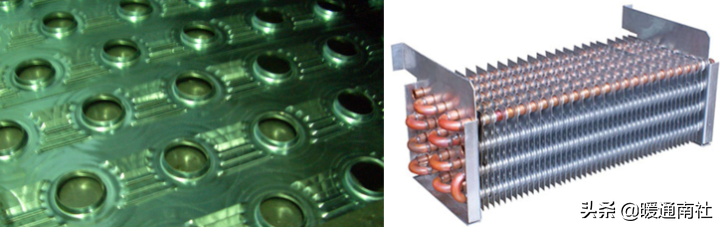
Air source heat pump water heater evaporator, all using tube and fin structure, more specifically, is a copper tube aluminum fin type, there are textbooks called "finned tube heat exchanger", or "ribbed tube heat exchanger".
Inside the tube of the evaporator is the process of Freon boiling and heat absorption, due to the low heat transfer coefficient of the air side, in order to increase the heat transfer capacity, the only way to strengthen the heat transfer coefficient and increase the heat transfer area without increasing the premise of the heat transfer temperature difference ΔT.
Schematic diagram of air-cooled evaporator structure:
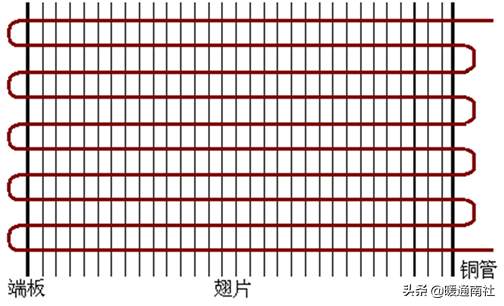
With the air conditioner outdoor fin and tube condensing heat exchanger is different, heat pump water heater evaporator is often in a wet state, in order to improve the heat transfer coefficient of the outer surface, conducive to the flow of condensate, to eliminate the phenomenon of the fins of the "water bridge" phenomenon, the evaporator's aluminum fins with "hydrophilic aluminum foil The aluminum fins of the evaporator are made of "hydrophilic aluminum foil".

The "air window" used to increase the air disturbance:
In order to reduce the flow resistance of the refrigerant in the evaporator, reduce the flow loss, the general evaporator will be divided into a number of roads in parallel into the evaporator, such as the above figure, the refrigerant is divided into four roads into the evaporator by the liquid dividing head, in order to ensure that the refrigerant flow in each road as far as possible the same flow rate, liquid dividing head of the copper tube after the same length, equal spacing, equal size, and the same course.
Various forms of evaporator:
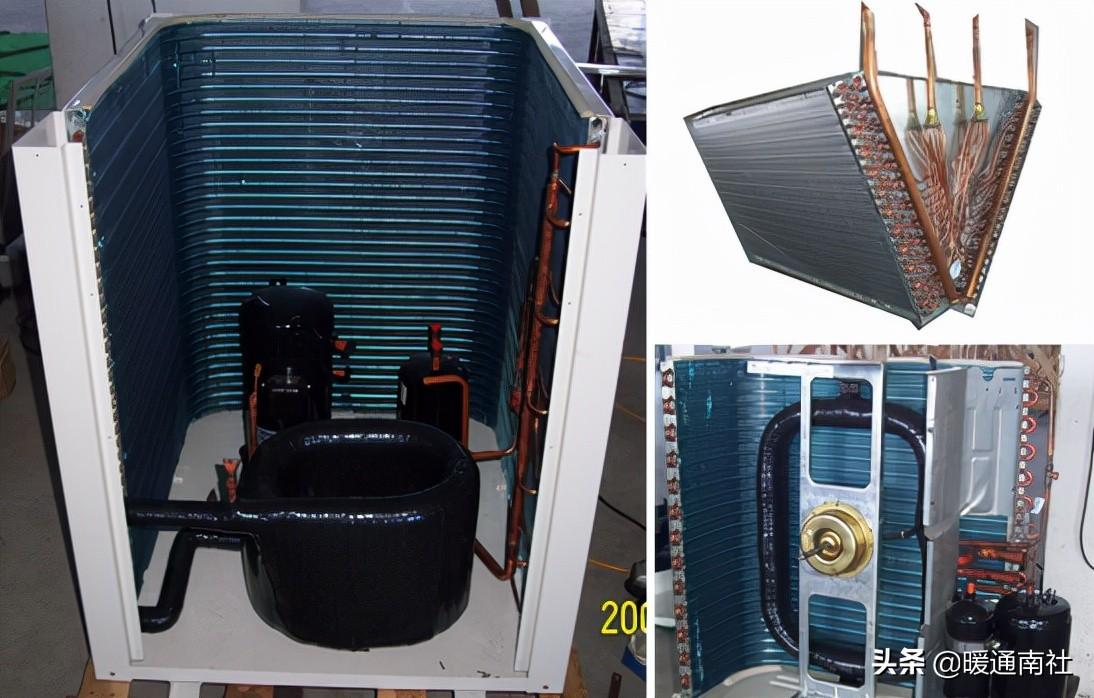

Motor and fan blade:

Fan facing can be upward and to the side:

Types and characteristics of heat pump condensers:
Can be divided into three broad categories:
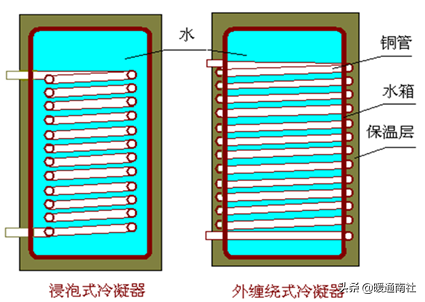
That is, all the volume of water directly heated volumetric condenser (static heating method);
Circulation heating type condenser (dynamic heating method) to all the water for circulation heating;
and direct-heat condenser that heats the water to a set temperature at one time and then transports it to the holding tank.
Two methods of arranging static heating condensers:
Circulating heating casing condenser:
Casing is widely used in heat pump water heaters;
Advantages are high efficiency, no operating dead zone, anti-scaling and anti-freezing ability, can be long-distance countercurrent type of high-efficiency heat exchanger; multi-bundle tube basic deactivation; disadvantage is that it occupies a large space.

Spiral tube type casing heat exchanger finished product and spiral tube and physical sectional drawing:

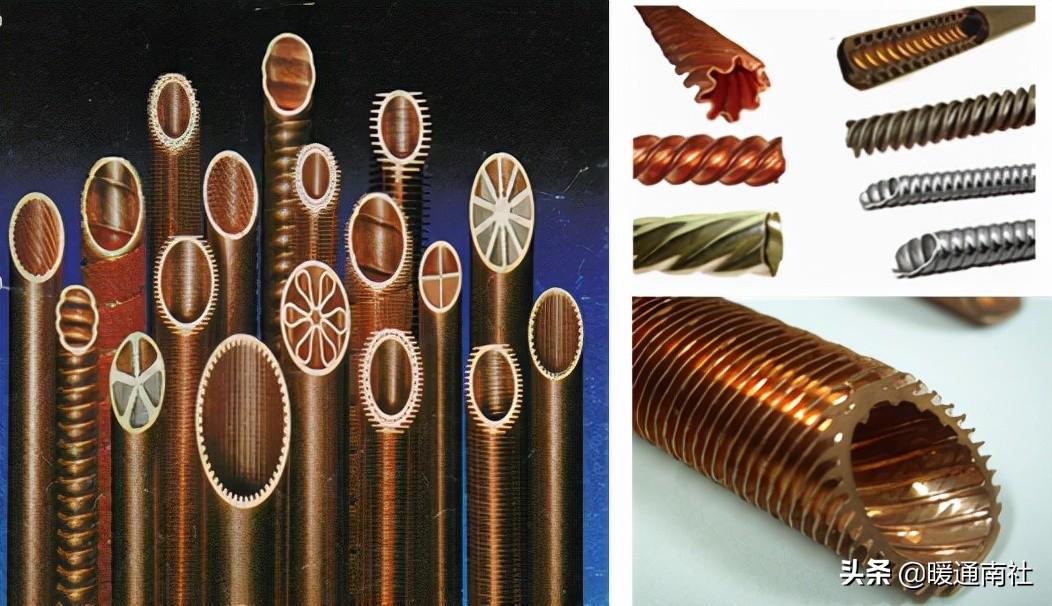
Various shaped copper tube:

Miniaturized shell and tube heat exchanger:
Copper ribbed tube coiled into a spiral ring placed in the steel tube tube - tube heat exchanger, water circulation in the copper tube, refrigerant flow in the steel tube, the steel tube plays a certain role in the reservoir. Occupies little space, but weak reverse heat transfer, not conducive to high temperature heating.

Plate heat exchanger:
By a series of metal sheets with a certain corrugated shape stacked into the formation of thin and narrow channels between the plates, heat exchange between the two adjacent pieces. It is compared with the conventional shell and tube heat exchanger, in the same flow resistance and pump power consumption, its heat transfer coefficient is higher.
Plate heat exchanger monolithic shape:
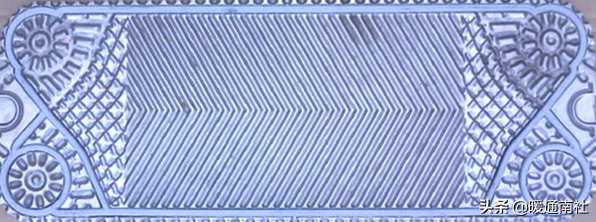
The flow route of the plate heat exchanger fluid:
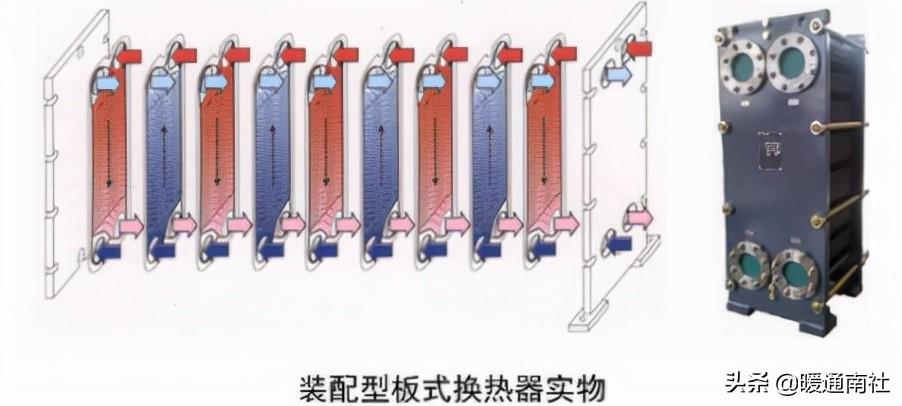
The assembled plate heat exchanger can be manufactured very large, so the heat transfer capacity is also large, and is widely used in ships, metallurgy, food, machinery, petrochemical industry, centralized heating and air conditioning in living areas.
It can also be used as a secondary heat exchanger for swimming pools, aquaculture and other purposes.
Shell and tube heat exchanger:
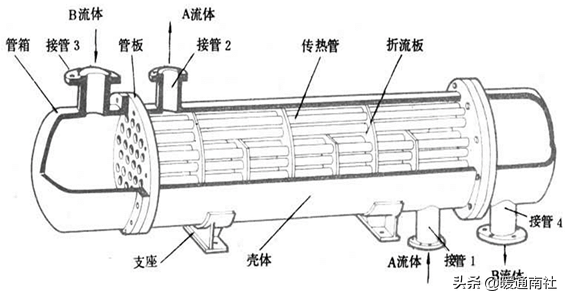
Mainly used for large refrigeration (heat pump) units:
Throttling device: capillary tube and expansion valve
Throttling device is one of the four indispensable parts of the refrigeration and heat pump system, which plays an important role in restricting the flow of refrigerant and establishing the difference between the high and low pressure of the system;
The structure of the throttling device can be extremely
General small heat pump system, the use of capillary tube; larger units using thermal expansion valve, electronic expansion valve.
Throttle adjustment:
Superheat, air conditioning terminology, is the dry saturated steam continues to be heated at constant pressure, the steam temperature is going to rise, and more than the saturation temperature, the temperature of its exceeding is called superheat.
Superheat (superheat) the term, used for thermal expansion valve is the temperature difference between the low-pressure side and the steam in the temperature-sensitive package. The system is usually regulated to operate at a superheat of (5-8°C).
The degree of superheat plays a pivotal role in the proper functioning of the expansion valve. Suction if there is no superheat at all, there is a possibility of liquid shock, causing wet stroke liquid shock damage to the compressor.
In order to avoid this phenomenon, a certain degree of suction superheat is required to ensure that only dry steam into the compressor (due to the nature of the refrigerant, the existence of superheat indicates the complete evaporation of liquid refrigerant).
However, a high degree of superheat will cause the compressor exhaust temperature (exhaust superheat) to increase, the compressor operating conditions deteriorate life reduced. Therefore, the suction superheat should be controlled in the range of 5℃-8℃.
Capillary tube:
Capillary tube, is a length of 0.5-5 meters ranging from 0.5mm-3mm inner diameter of the thin copper tube, the structure is very simple, reliable, low-cost, no moving and sealing parts itself, welded between the condenser and the evaporator, generally will not leakage and other failures, capillary tube has a certain degree of automatic adjustment of refrigerant flow, when the pressure difference increases the ability to increase the flow of refrigerant, so that the system is balanced to some extent. The system is balanced to a certain extent;

Thermal expansion valve:
Thermal expansion valve: thermal expansion valve, also known as temperature-sensitive adjustment valve or automatic adjustment valve, it can flow out of the evaporator according to the temperature of the refrigerant to regulate the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, thermal expansion valve, according to the different types of flow regulation is divided into internal balanced expansion valves and external balanced expansion valves.
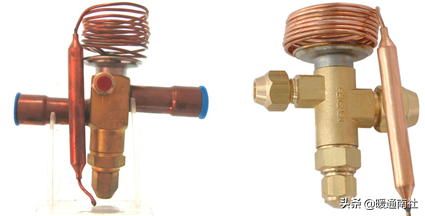
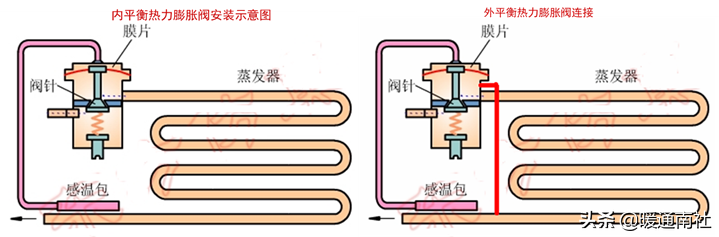
Expansion valve installation method in the system:
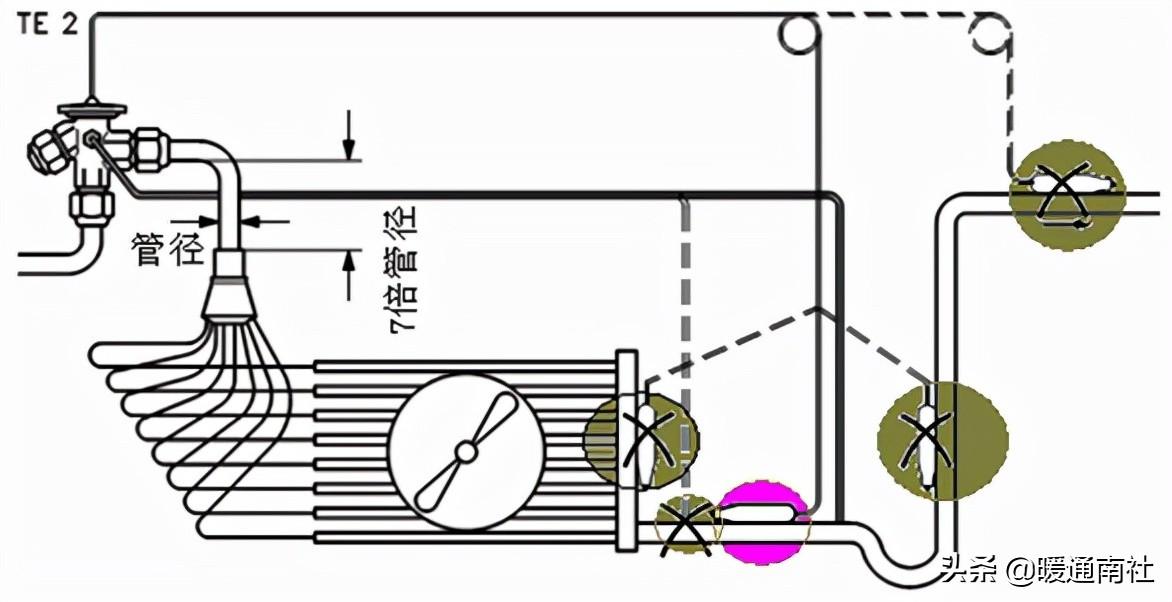
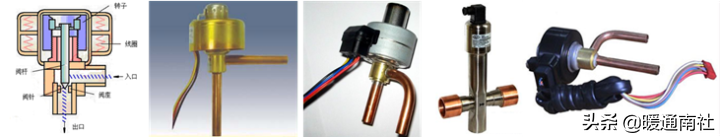
Electronic expansion valve:
Electronic expansion valve, is the use of electrical signals to directly control the current or voltage on the expansion valve to change the needle valve movement of the throttle device, sensitive and accurate response, flow control range, can be predetermined procedures, in accordance with the actual work of the system evaporator signal control;
According to the type of actuator is divided into electromagnetic and electric two types.
The heat pump water heater system mostly adopts electric type.
Electric electronic expansion valve structure schematic:
Electronic expansion valve opening degree can be accurately adjusted within the range of 0-100%, from fully closed to fully open state can be completed in a very short period of time, fast response and action speed, opening and closing characteristics and speed can be set in the control program. In the degree of frost is not very serious area, can also be bypass defrost with the electronic expansion valve fully open.
Heat pump water heater using electronic expansion valve, generally controlled by the suction superheat, by the pressure sensor and temperature sensor to provide signals, the controller to perform the adjustment action; work, the pressure sensor will evaporator outlet pressure signal, temperature sensor compressor suction temperature signal to the controller, the controller will signal processing, the output of electrical impulses act on the electronic expansion of the stepper motor, the valve will be adjusted to the required Position.
Electronic expansion valve can be pre-programmed in advance, under various operating conditions to accurately control the throttle state, to improve the system's energy efficiency and reliability. For heat pump water heater such a wide range of operating temperature devices, should consider the use of electronic expansion valves, in the selection of each working condition should be fully matched with the experiment.
Four-way valve: four-way valve is a heat pump water heater system defrost, used to change the refrigerant flow direction of the device.
Air source heat pump water heater, there are many kinds of defrosting methods, such as bypass defrosting, electric defrosting, hot water defrosting, etc., but the four-way valve recoil defrosting is the most important method;
In the heat pump water heater normal heating, the four-way valve coil is not energized, the direction of its assembly, just the opposite of the air conditioner.
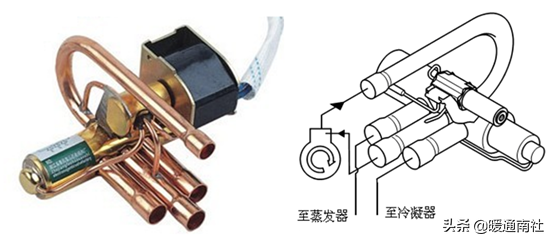

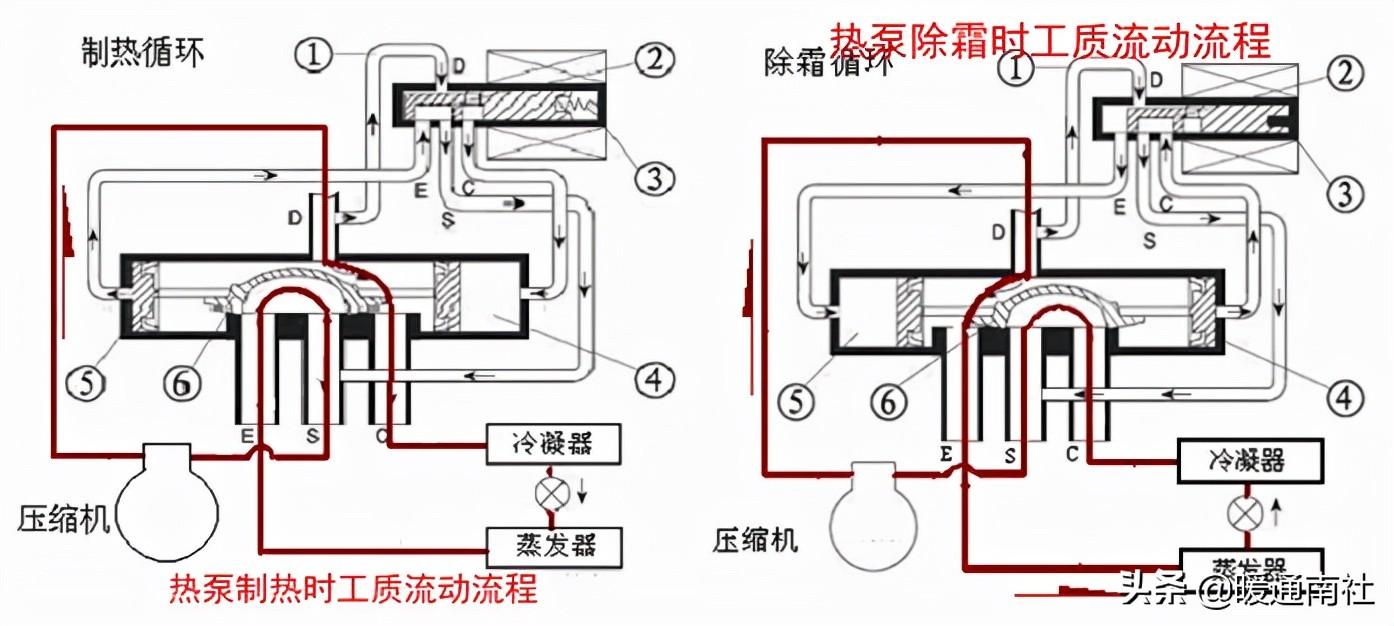
The four-way valve is an important part of the air source heat pump water heater for defrosting in the cold season;
However, the four-way valve can be left out on units using other methods such as bypass defrosting, electric defrosting and natural defrosting.
Using direct heat heating method of







